Gas drilling is a drilling operation that uses gas instead of drilling fluid as the circulating flow medium. Gas has the characteristics of low density, low viscosity, and low pressure on the wellbore. It is the earliest developed underbalanced drilling technology. The use of gas drilling can greatly increase the mechanical speed and protect the production layer.
This technology is widely used in the drilling and development of oil and gas wells (including coalbed methane) in various places. Since the past, gas drilling has been mainly used in medium and low pressure formations, which can greatly increase the drilling speed and prevent lost circulation.
In recent years, with the development of a large number of low-permeability oil and gas reservoirs, how to protect such reservoirs has become the focus of attention. Gas drilling has obvious advantages over traditional drilling methods for protecting low-permeability oil and gas reservoirs. At the same time, gas drilling also has other characteristics such as greatly increasing drilling speed, reducing drilling cost, and less environmental pollution.
1. Overview of Gas Drilling
| Topic |
Information |
| Wellhead Surface Control for Gas Drilling |
Effective wellbore fluid control at wellhead is vital in gas drilling; selection of wellhead, control device, and manifold must meet pressure and flow requirements, proven safety. |
| Installation of Gas Drilling Equipment |
Installing air drilling equipment involves connections (flow meter, relief valve), supply pipelines, drilling floor manifold. |
| Installation of Rotary Control Head |
Properly center rotary control head near turntable; ensure kelly and drill pipe surfaces are in good condition. |
| Installation of Discharge Pipeline |
Straight discharge line installation to prevent damage from high-speed debris; install pressure relief, sample capture, and ignition devices. |
| Gas Lift |
Gas lift preparations include casing pressure testing, bottom cleaning, replacing fluid with water, no power tools downhole. |
| Drilling |
Pre-drilling setup includes cock and check valve, open gate valves, and testing drilling parameters; monitor variables and report abnormalities during drilling. |
| Drilling Directional Wells |
Increase measurement frequency in easily deviated sections, lower inclinometer for measurement, monitor drilling tool movement during directional drilling. |
Gas Drilling Is Especially Suitable for the Following Situations
-
hard rock
-
Well wall stability is strong;
-
Less formation fluid invasion;
-
Formation with low to medium pore pressure;
-
Water-scarce and dry areas;
-
Formation sensitive to water-based or oil-based drilling fluids.
Limitations of Gas Drilling
-
The intrusion control of formation fluid is not strong;
-
The scope of application of the drill bit is narrow. Because the cooling effect of air on the drill bit is not strong, diamond drill bits with low high temperature resistance are seldom used in air drilling, so roller cone bits are mostly used in air drilling;
-
Soft formations are not suitable for air and gas drilling. Generally, the cuttings produced in soft formations are large in size, which is not conducive to gas carrying cuttings at large well depths;
-
The bottom of the well is on fire. When the bottom hole hydrocarbon gas is mixed with air to a certain ratio, combustion may occur. The branch horizontal well is used, that is, the auxiliary wells are drilled from the main wellbore in all directions to the production layer to a depth of more than 100 meters. These auxiliary wellbores are used as oil drainage channels to connect the large oil reservoirs that have not been put into development between ordinary wells.
In terms of economic effects In other words, its value is equivalent to opening a new oil field in a fully constructed mine area. It is a technically feasible and more economically attractive method to use the original wellbore sidetracking horizontal wellbore for secondary completion in mature oilfields.
2. Gas Drilling Technology
Wellhead Surface Control for Gas Drilling
In conventional drilling, the entry of formation fluids into the wellbore is controlled, while in gas drilling, the formation is allowed to enter the wellbore. Therefore, in gas drilling, it is extremely important to effectively control the fluid entering the wellbore at the wellhead and on the ground. The selection of gas drilling wellhead, surface control diversion device and manifold must meet the following principles:
Installation of Gas Drilling Equipment
The installation of air drilling equipment mainly includes: the connection between equipment, including the connection of flow meter, pressure relief valve and bypass valve, etc.; the main supply pipeline from the equipment to the drilling rig; the drilling floor manifold includes the bypass pipeline and the discharge pipeline.
Oil supply system: mist pump – so that it can start working in the shortest time when needed.

Installation of Rotary Control Head
The rotary control head should be as close as possible to the turntable, and must be centered in line with the turntable. With top drives, the centering of the rotary control head is also critical. Make sure that the kelly and drill pipe surfaces are in good condition and free from pinch marks, as this will shorten the life of the insert.

Installation of Discharge Pipeline
-
Install the discharge line as straight as possible. Due to the impact of rock debris returning from the annulus at high speed, the bends of the pipeline will be quickly damaged by erosion.
-
Simultaneously install kelly pressure relief pipeline, rock sample capture device and discharge pipeline ignition device.
Gas Lift
-
Before gas lift, pressure tests the casing and wellhead according to the design requirements;
-
Drill through the casing guide shoe, fully circulate, and clean the bottom of the well;
-
Replace the drilling fluid in the well with clean water before gas lift;
-
Gas lift drilling tools shall not carry downhole power drilling tools;
-
Before gas lift, calculate the running depth of the drilling tool according to the well depth and the rated pressure of the supercharger;
-
Before gas lift, close the sluice width from the standpipe to the pump room, the semi-sealed ram BOP and the gate valve on the discharge pipeline to the combustion pool, open the hydraulic flat valve at the front end of the throttle manifold and the valve to the sewage The gate valve on the pipeline of the pool and the outlet pipeline should be fixed firmly;
-
After downhole gas lift is completed, increase the gas injection rate and fully circulate until there is no liquid drop at the outlet.
Drilling
-
Before drilling, connect a lower cock and a normally closed cobalt tool check valve on the drill pipe and enter the well with the drilling tool (the cock is down);
-
When drilling, the gate valves in the middle of the drilling choke manifold are in the open state: the hydraulic flat valve in front of the drilling choke manifold is in the closed state;
-
Test drilling should be carried out in the early stage of drilling to adjust the reasonable matching of drilling parameters;
-
Brake lever operators are required to concentrate and send the drill evenly; pay close attention to the changes in the injection pressure, gas injection volume, drilling time, turntable torque, gas detection hydrocarbon value, cuttings, and returned dust during drilling, and find abnormalities Timely report and timely processing;
-
The pressurized gas supply button and the drill floor operators clearly and uniformly supply and stop the gas signal;
-
When drilling directional wells, the inclination measurement frequency of the easily deviated well section should be increased; when the inclination is lower than 65°, the inclinometer should be lowered to the bottom of the well for inclination measurement with a winch; Pull out the drill, put the inclinometer into the inclinometer seat, and then use the drilling tool to send it to the bottom of the well, and start the inclinometer for a short time;
- After drilling into the gas layer, stop the gas injection, and lift the drilling tool to the safe well section.
3. Matters Needing Attention to Gas Drilling Construction
Drilling Fluid Replacement and Wellbore Drying
The preparation work for gas drilling is to hollow out the wellbore and dry the wellbore. First, determine the lifting height according to the highest gas injection pressure and drilling fluid density that the gas injection equipment can provide; use the well control device to control the pressure during the gas lift process to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment, and thoroughly dry the well wall after replacement.
The purpose of drying the well wall is not only to ensure smooth circulation without the formation of new filter cakes, but also to ensure the stability of the well wall.
Drilling
The main goal of the drilling stage is to increase the ROP and drilling time as much as possible under the condition of controlling the well deviation. There is no holding effect, and the ROP is obviously improved. With the increase of the WOB, the drilling time is obviously reduced; however, the effect is not obvious when the WOB increases to a certain value. Gas drilling generally adopts a tower drilling tool structure, which does not have the ability to correct and prevent deflection.
Therefore, in order to achieve the purpose of improving drilling efficiency, firstly, it is necessary to optimize the drilling parameters and drilling tool structure to ensure a high ROP; drilling to reduce the occurrence of well deviation, and at the same time strengthen the wellbore trajectory monitoring to ensure the wellbore trajectory control requirements.

Handling of Abnormal Situations
Formation Water
After the water came out of the strata, the cuttings returned had some changes, and the phenomenon of falling blocks was obvious. If there is no significant change in torque and gas injection pressure, it means that the water output is very limited, and you can observe it cyclically.
If everything is normal, you can continue drilling. If the water production is large, the torque and gas injection pressure will increase rapidly, and improper handling may cause downhole complex accidents such as pipe sticking.
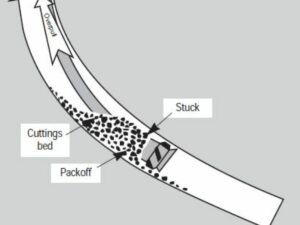
Drill Sticking Phenomenon
There are three main causes of drill sticking:
-
A large amount of water is produced in the formation, and the water and rock cuttings are mixed to form mud and filter cake, and the mud packs the drilling tool, blocking the air flow channel;
-
Concurrent explosions lead to partial well wall collapse;
-
Drilling encounters an unstable well section, and the well wall collapses. Therefore, attention should be paid to these matters during drilling to reduce the occurrence of accidents.
4. Conclusion
Gas drilling should be combined with the actual production, based on the actual production of oilfields, from which valuable geological and experimental air drilling data can be obtained, which meets the needs of exploration and development work and conforms to the development trend of exploration and development, and is of practical significance and forward-looking
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse product options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available to assist and g